There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
NCERT Science Notes - Class 9
Chapter 1 - Matter in our surroundings
Welcome to AJs Chalo Seekhen. This webpage is dedicated to Class 9 | Science | Chapter 1 - Matter in our surroundings. The chapter delves about matter, which has mass and occupies space. This chapter explains the three states of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—and their characteristics. It highlights how temperature and pressure affect these states and includes concepts like evaporation and condensation. Understanding the behavior and properties of particles of matter forms the basis of this chapter, providing students with essential knowledge about the physical world and preparing them for more advanced topics in chemistry and physics. This foundational chapter equips students with the tools to explore and understand matter deeply.
NCERT Science Notes - Class 8 Chapter 9 - Friction notes ajs, cbse notes class 10 ajslearning, cbse notes ajs, ajs notes class 10, ajslearning, ajs chalo seekhen
NCERT Science Notes - Class 9
Chapter 1 - Matter in our surroundings
What is Matter?
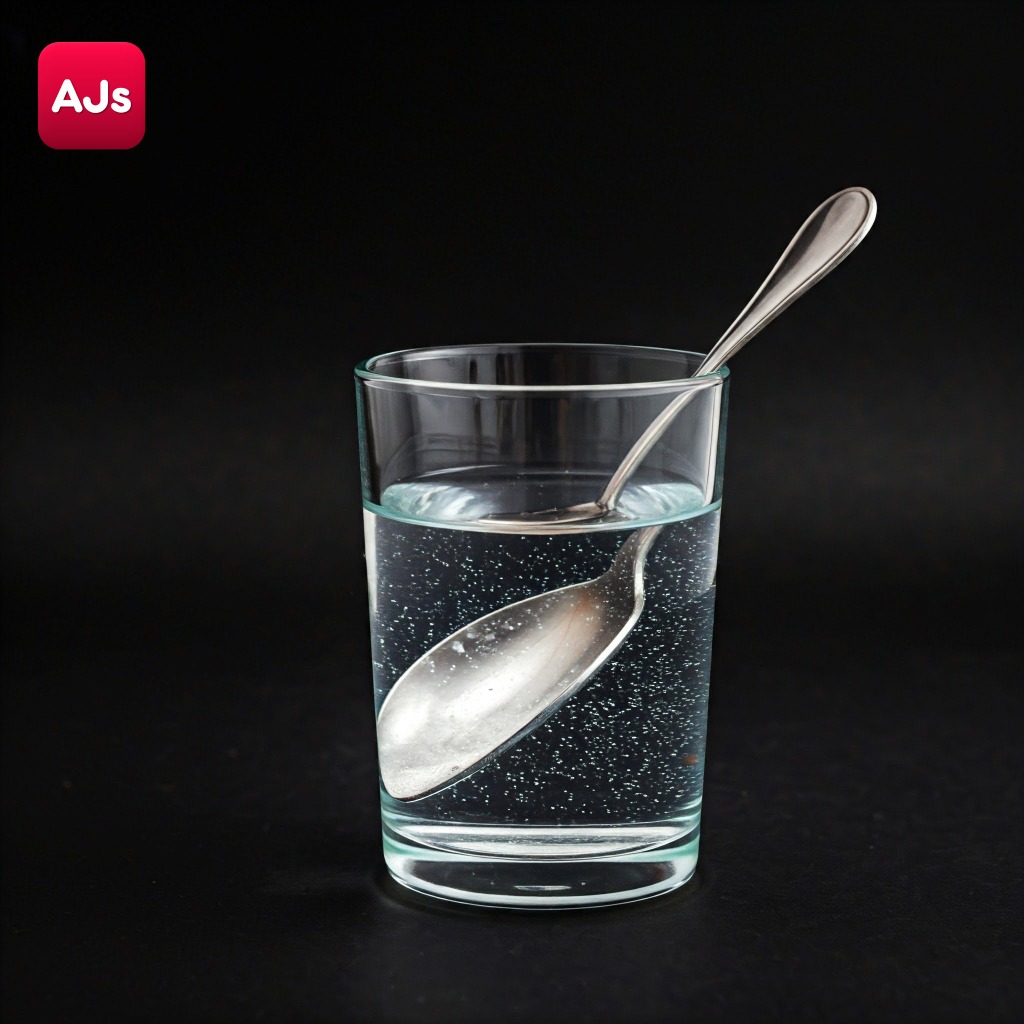
Activity 1.2: Observing the Smallness of Particles
Objective: To observe how particles of different substances (ink and honey) move in water and spread over time, demonstrating the movement of particles in matter.
Materials:
1.2.1 - Particles of Matter Have Space Between Them
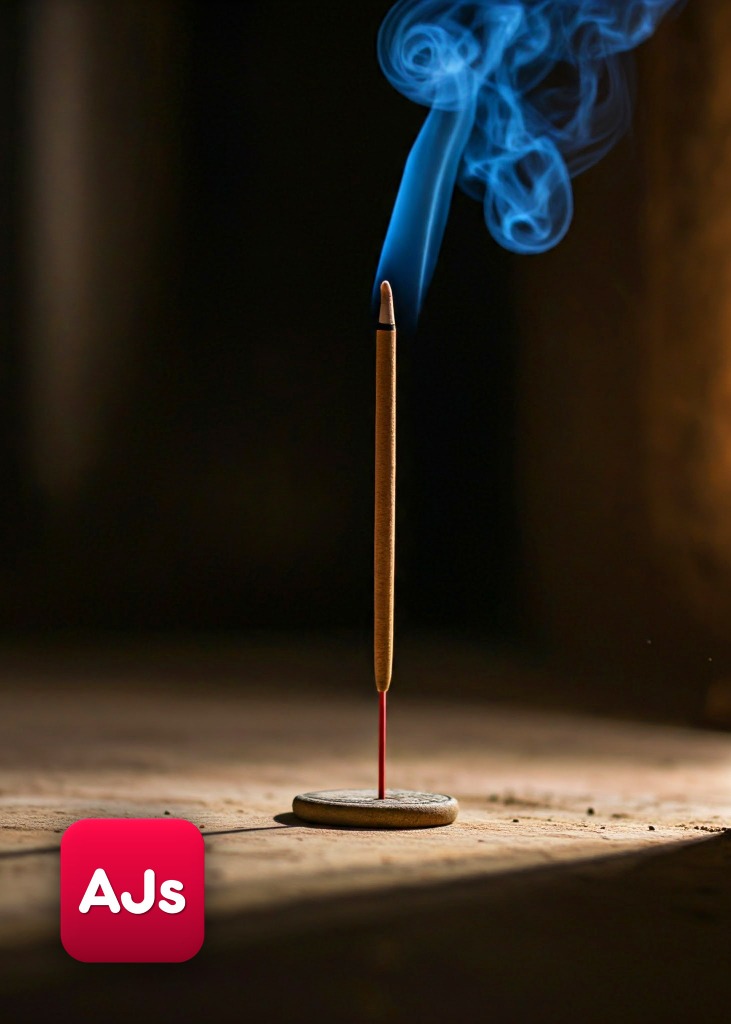
Activity 1.3: Observing the Movement of Particles Using an Incense Stick
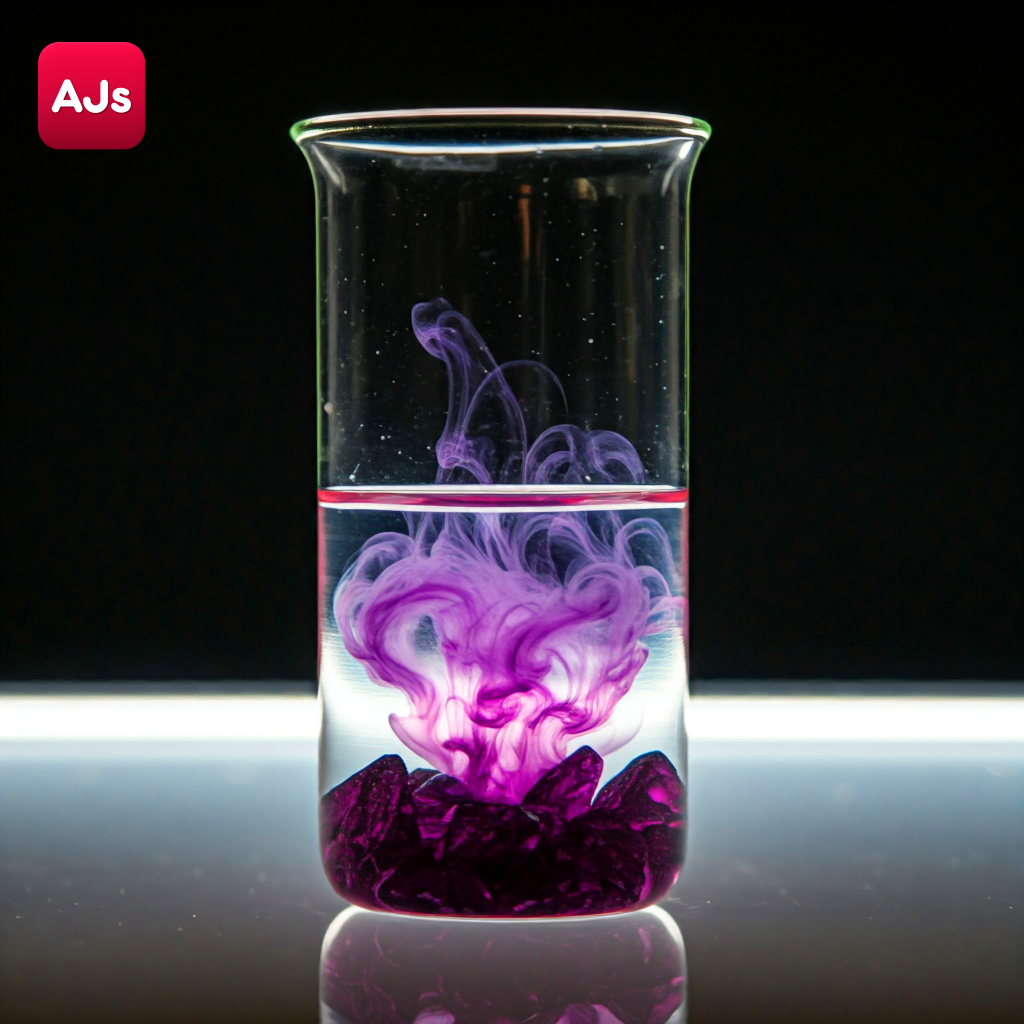
Objective: To observe how the rate of diffusion changes with temperature using copper sulphate or potassium permanganate crystals.
Materials:
Activity 1.6: Human Chain Game
Objective: To observe how particles of matter attract each other by comparing the strength of connections between human chains.
Materials:
Activity 1.7: Breaking Different Materials
Objective: To observe the varying forces of attraction between particles in different materials.
Materials:
Activity 1.8: Surface Tension of Water
Objective: To observe the attraction between particles of water at the surface.
Materials:
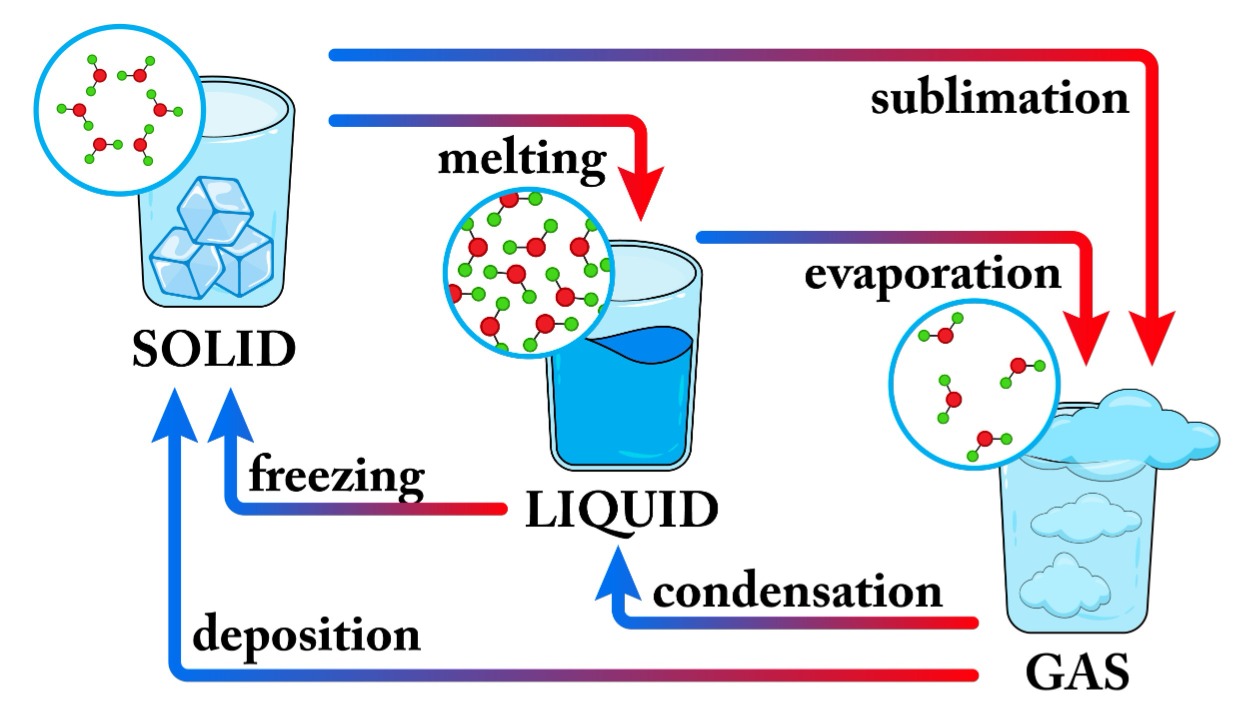
Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. These states arise due to differences in the properties of the particles that make up matter. Let’s explore the solid state first.
1.3.1 - The Solid State
Objective: To study the properties of solids by examining common objects.
Materials:
In the liquid state, matter exhibits different characteristics compared to solids. Liquids do not have a fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They flow easily and take the shape of the container they are placed in.
Activity 1.10: Exploring the Properties of Liquids
Objective: To observe how liquids behave when transferred between containers and spilled, and to understand their flow and shape properties.
Materials:
Gases, unlike solids and liquids, exhibit unique properties such as high compressibility and rapid diffusion. These characteristics are due to the large spaces between gas particles and their fast, random movement.
Objective: To compare the compressibility of solids, liquids, and gases by observing their behavior in a syringe.
Materials:
Matter can indeed exist in different states: solid, liquid, and gas. Water is a common example, which can exist as:
1.4.1 - Effect of Change of Temperature
Activity - 1.12
Objective: To observe the effect of temperature on the change of state from solid to liquid and liquid to gas.
Effect of Temperature on State of Matter
When the temperature of a solid is increased, the kinetic energy of its particles increases. As a result, the particles begin to vibrate more rapidly. When sufficient heat is supplied, the energy overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles, allowing them to break free from their fixed positions. At this stage, the solid begins to melt and converts into a liquid.
Melting Point:
Materials Needed:
The state of matter can be changed not only by changing the temperature but also by applying pressure. The main difference between different states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) lies in the distance between particles. When pressure is applied to a gas, it compresses, and the particles come closer.
What happens when we compress a gas?
When pressure is applied to a gas enclosed in a cylinder, the particles of gas come closer to each other. If we increase the pressure and reduce the temperature sufficiently, the gas can liquefy, changing from the gaseous state to the liquid state.
Example of Solid Carbon Dioxide (Dry Ice):
We have already seen how matter changes state through heating or by applying pressure. However, there are everyday examples where liquid changes into vapour without the liquid reaching its boiling point.
Examples:
Why Does Evaporation Occur?
The particles of matter are always in motion and have varying amounts of kinetic energy. In liquids, especially at the surface, some particles possess enough kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction from other particles. These high-energy particles escape the surface of the liquid and turn into vapour.
Definition of Evaporation:
Evaporation is the change of a liquid into vapour at a temperature below its boiling point. It occurs when surface particles with higher kinetic energy break free from the liquid and enter the gaseous phase.
Key Points:
Evaporation can be influenced by various environmental factors. Let's explore these factors through the activity and observations:
Activity:
Evaporation leads to cooling because the particles of a liquid absorb energy from their surroundings in order to transition from a liquid state to a vapour state. This absorption of energy results in a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings, causing a cooling effect.
NCERT Science Notes - Class 9 Chapter 1 - Matter in our surroundings
NCERT Science Notes - Class 9 Chapter 1 - Matter in our surroundings
Dedicated team provides prompt assistance and individual guidance.
Engaging visuals enhance understanding of complex concepts.
Engaging visuals enhance understanding of complex concepts.
Assess understanding and track progress through topic-specific tests