There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
NCERT Science Notes - Class 10
Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Welcome to AJs Chalo Seekhen. This webpage is dedicated to Class 10 | Science | Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals. The chapter delves into the properties and reactions of metals and non-metals. It explores their physical and chemical properties, how metals react with oxygen, water, dilute acids, and other metal salts, forming various compounds and exhibiting different behaviors. The chapter also discusses the concept of a reactivity series, where metals are arranged based on their reactivity levels. Additionally, it examines the nature of metal oxides and how metals displace one another in compounds, a process known as the displacement reaction. This chapter provides foundational knowledge of metals and non-metals, which is crucial for understanding various chemical processes and the principles of inorganic chemistry.
Class 10 NCERT metals and non metals notes ajs, cbse notes class 10 ajslearning, cbse notes ajs, ajs notes class 10, ajslearning, ajs chalo seekhen
NCERT Science Notes - Class 10
Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Activity 3.4
Activity 3.5
Activity 3.7
Observations for Non-Metals:
Table 3.1: Observations for Metals and Non-Metals
| Element | Symbol | Type of Surface | Hardness | Malleability | Ductility | Conducts Electricity | Sonority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | Fe | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Copper | Cu | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Aluminum | Al | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Magnesium | Mg | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Sodium | Na | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Lead | Pb | Dull | Soft | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Zinc | Zn | Shiny | Hard | Malleable | Ductile | Yes | Yes |
| Carbon | C | Not Shiny | Not Hard | Not Malleable | Not Ductile | No | No |
| Sulphur | S | Not Shiny | Not Hard | Not Malleable | Not Ductile | No | No |
| Iodine | I | Shiny | Not Hard | Not Malleable | Not Ductile | No | No |
Discussion:
Activity 3.8
Section Overview
General Reaction of Metals with Oxygen:
Specific Examples and Reactions:
Nature of Metal Oxides:
Reactions of Amphoteric Oxides:
Solubility and Reaction with Water:
Reactivity and Protective Layers:
In summary, anodising is a valuable industrial process for improving the durability and aesthetic appeal of aluminium products. Observations from educational experiments like Activity 3.9 are crucial in teaching students about the reactivity of metals, although not all reactivity levels can be conclusively determined from such simple experiments. Further investigation is needed to accurately place metals in a reactivity series.
Activity 3.11
Interesting Fact (Aqua Regia):
Activity 3.12
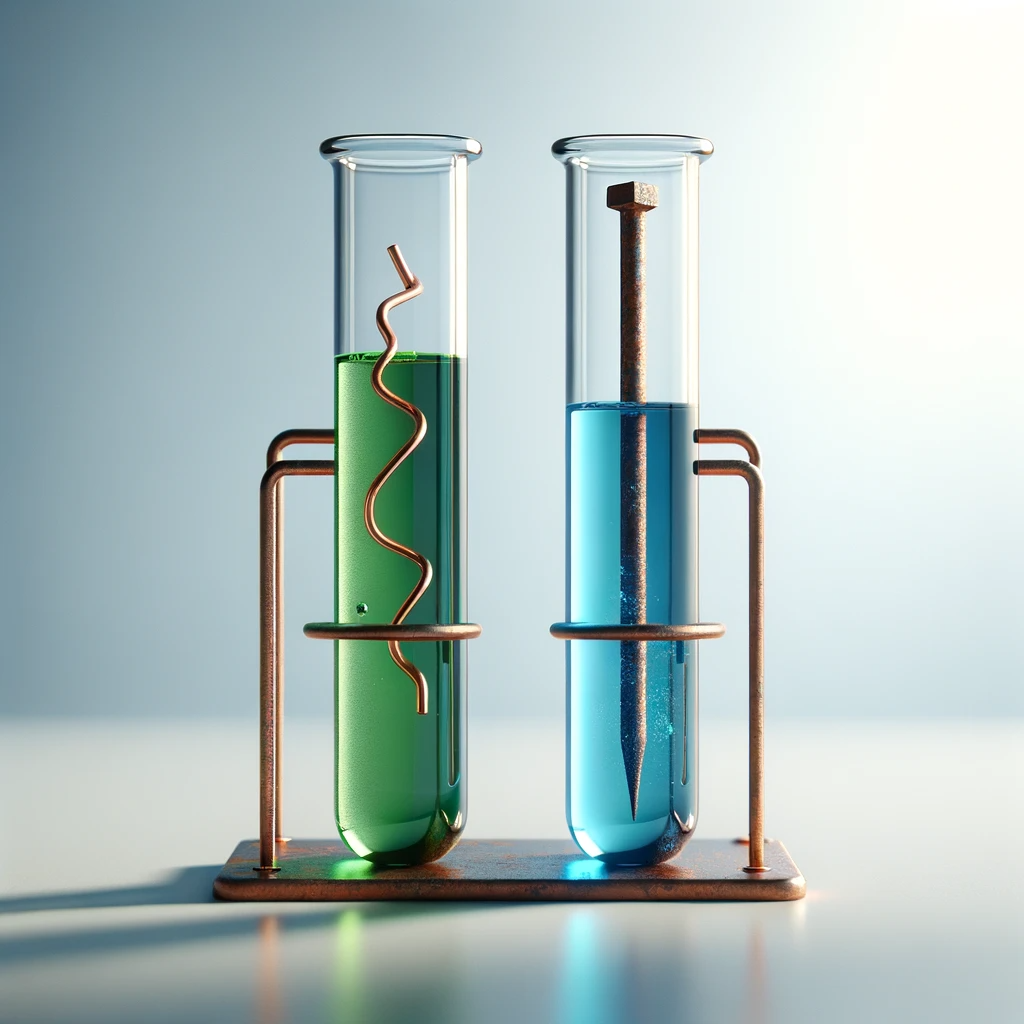
Through Activity 3.12, students can witness firsthand the displacement reactions between metals and metal salt solutions. This activity helps in understanding the concept of reactivity series, which ranks metals based on their ability to displace others from their compounds. The reactivity series is an important concept in chemistry that explains the outcomes of various reactions, including those with oxygen, water, and acids, as explored in previous activities (3.9, 3.10, and 3.11).
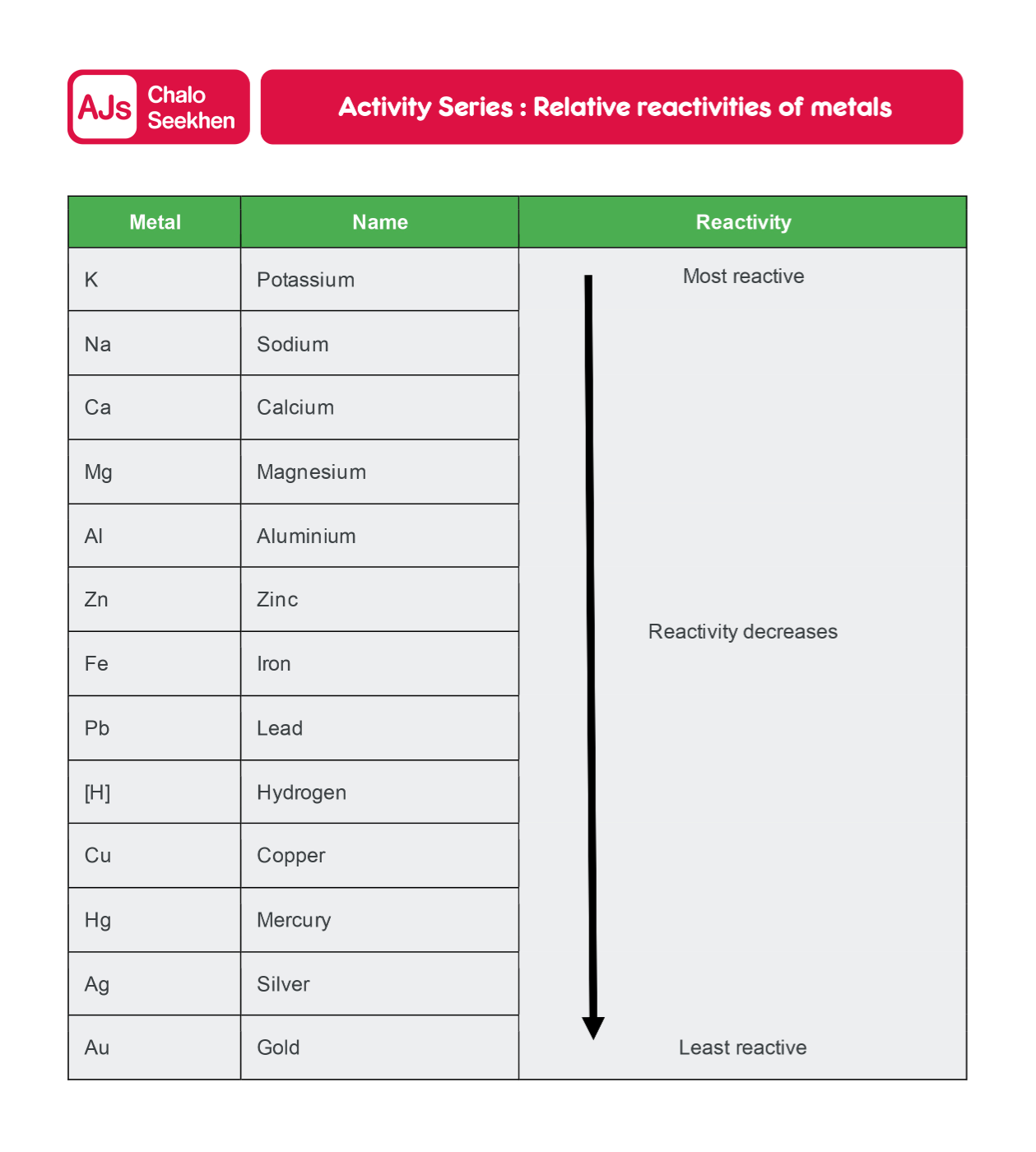
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities. After performing displacement experiments (Activities 1.9 and 3.12), the following series, known as the reactivity or activity series, has been developed.
Table 3.2 Activity Series: Relative Reactivities of Metals
This series is fundamental in understanding the behavior of metals in various chemical reactions, including their interactions with water, acids, and other metal salts.
Electronic Configurations:
Formation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl):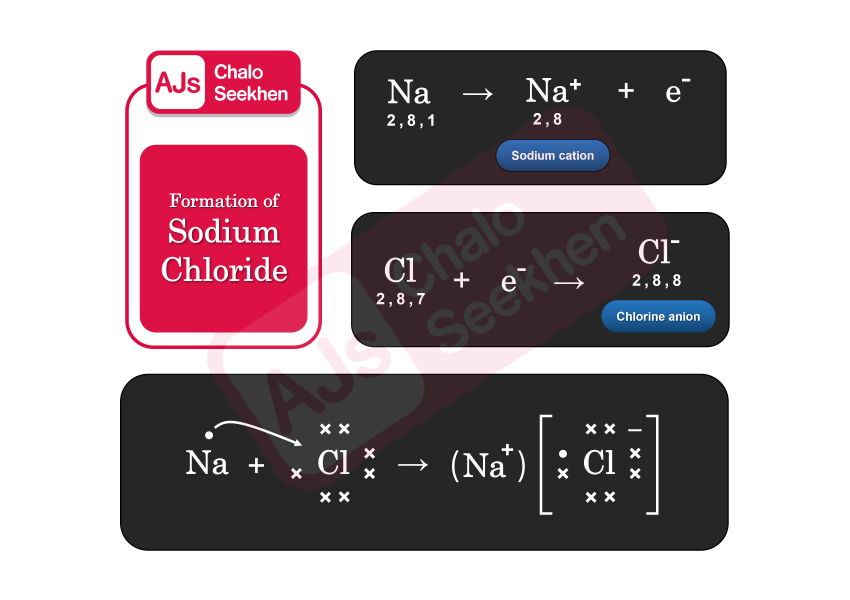
Formation of Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2):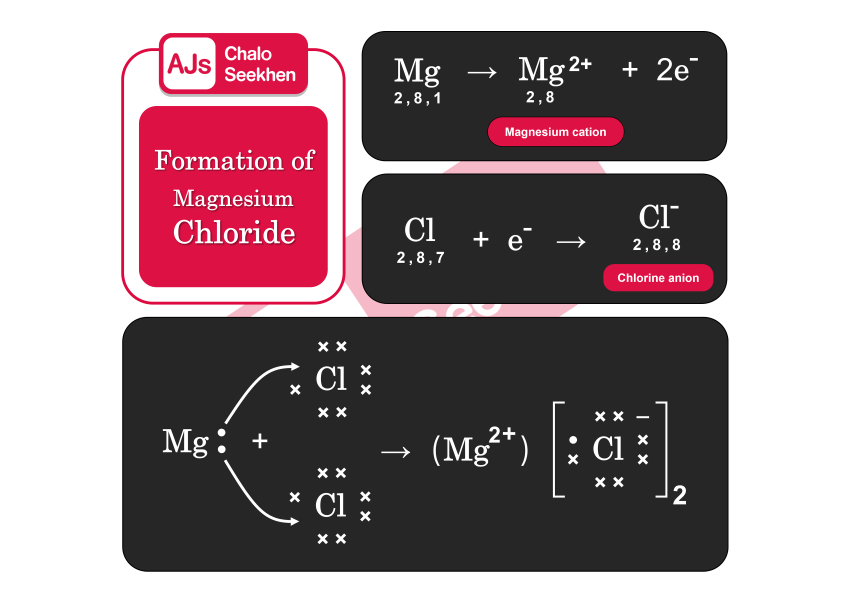
Ionic Compounds:
Electronic Configurations of Some Elements (Table 3.3):
| Type of Element | Element | Atomic Number | Number of Electrons in Shells | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | L | M | N | |||
|
|
Helium (He) | 2 | 2 | |||
| Neon (Ne) | 10 | 2 | 8 | |||
| Argon (Ar) | 18 | 2 | 8 | 8 | ||
|
|
Sodium (Na) | 11 | 2 | 8 | 1 | |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 12 | 2 | 8 | 2 | ||
| Aluminium (Al) | 13 | 2 | 8 | 3 | ||
| Potassium (K) | 19 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 1 | |
| Calcium (Ca) | 20 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 2 | |
|
|
Nitrogen (N) | 7 | 2 | 5 | ||
| Oxygen (O) | 8 | 2 | 6 | |||
| Fluorine (F) | 9 | 2 | 7 | |||
| Phosphorus (P) | 15 | 2 | 8 | 5 | ||
| Sulphur (S) | 16 | 2 | 8 | 6 | ||
| Chlorine (Cl) | 17 | 2 | 8 | 7 | ||
|
Table 3.4 Melting and boiling points of some ionic compounds |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ionic compound | Melting point (K) | Boiling point (K) |
| NaCl | 1074 | 1686 |
| LiCl | 887 | 1600 |
| CaCl2 | 1045 | 1900 |
| CaO | 2850 | 3120 |
| MgCl2 | 981 | 1685 |
You may have observed the following general properties for ionic compounds —
Notes for Understanding:
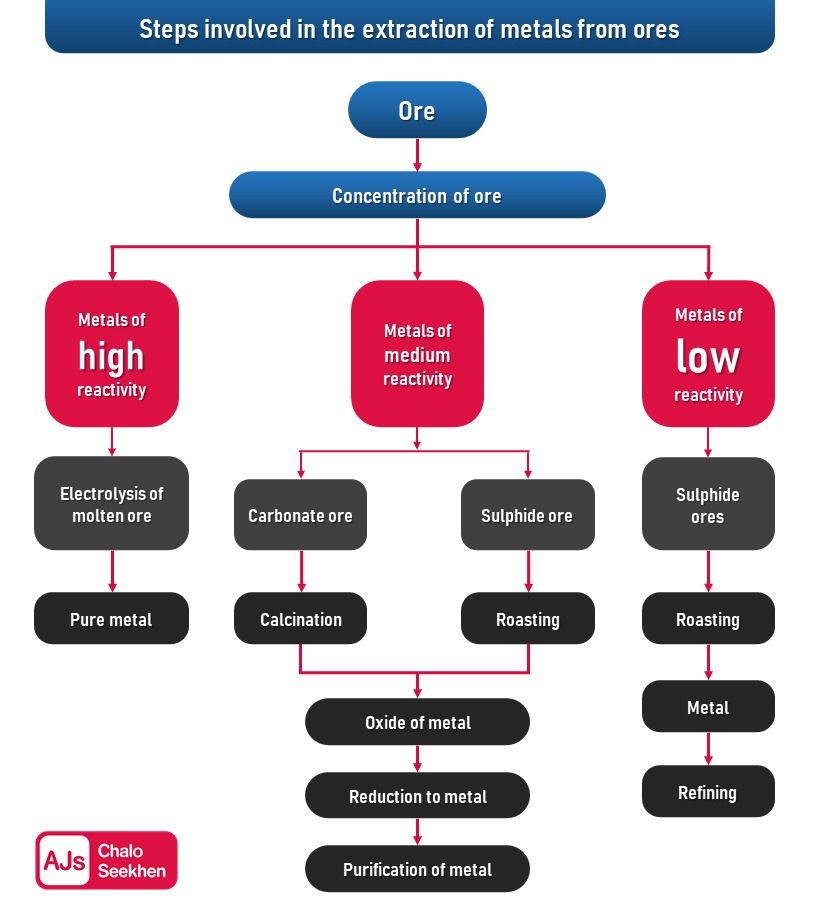
Metals like sodium, magnesium, and calcium are obtained through the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. During this process:
Example Reactions:
At cathode: Na+ + e– → Na
At anode: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Aluminium is obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide.
Note: Metals obtained through various reduction processes contain impurities and require refining to achieve purity.
This is a widely used method for refining metals like copper, zinc, tin, nickel, silver, and gold. The process involves:
During electrolysis:
Notes for Understanding:
Experiment to determine the conditions for iron rusting:
After a few days, observe the changes:
Notes for Understanding:
Corrosion, especially rusting of iron, can be prevented by several methods. Understanding these can help in prolonging the life of metal objects.
The Iron Pillar near Qutub Minar in Delhi: A testament to ancient Indian metallurgy, this iron pillar is over 1600 years old and is renowned for its rust resistance. Weighing 6 tonnes and standing 8 meters tall, it showcases the advanced ironworking skills of ancient Indian craftsmen.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals Notes

AJs Chalo Seekhen Class 10 NCERT Notes Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals AJs Chalo Seekhen Class 10 CBSE Notes Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals ajs Notes Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals ajs class 10 Notes Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Dedicated team provides prompt assistance and individual guidance.
Engaging visuals enhance understanding of complex concepts.
Engaging visuals enhance understanding of complex concepts.
Assess understanding and track progress through topic-specific tests